Abstract
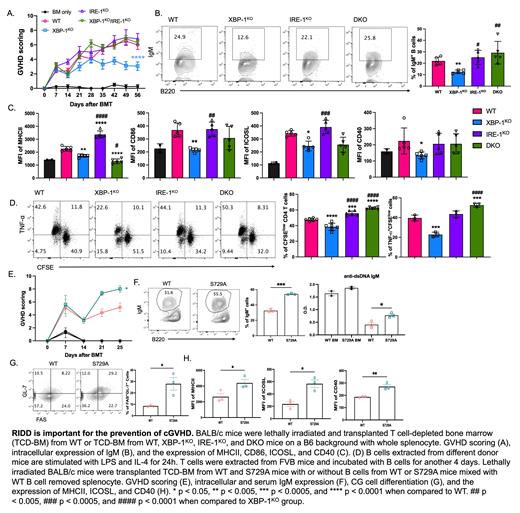
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HCT) is an effective therapeutic procedure to treat hematological malignancies. However, the benefit of allo-HCT is limited by a major complication, chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD). Since transmembrane and secretory proteins are generated and modified in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the ER stress response is of great importance to secretory cells including B cells. By using conditional knock-out (KO) of XBP-1, IRE-1α or both specifically on B cells, we demonstrated that the IRE-1α/XBP-1s pathway, one of the major ER stress response mediators, plays a critical role in B cell pathogenicity on the induction of cGVHD in murine models of allo-HCT. Endoribonuclease activity of IRE-1α not only activates XBP-1s transcription factor by converting unspliced XBP-1 (XBP-1u) mRNA into spliced XBP-1 (XBP-1s) mRNA but also cleaves other ER-associated mRNAs through regulated IRE-1α-dependent decay (RIDD). Besides, it is known that ablation of XBP-1s production leads to unleashed activation of RIDD. Therefore, we hypothesized that RIDD plays an important role in B cells during cGVHD development. In this study, we found that B cells deficient for XBP-1s reduced ability to induce cGVHD, which however was reversed by inactivation of IRE-1α, highlighting the role of RIDD in controlling cGVHD (Fig. A). Activation of RIDD targets IgM mRNA of (Fig. B), a contributor to organ damage and fibrosis in cGVHD, which correlated with dysregulated expression of MHC II and costimulatory molecules such as CD86, CD40, and ICOSL in B cells (Fig. C). Alloreactive T cells need to be primed by APCs to initiate GVHD, and specifically, CD86 and CD40 mediated-costimulation from APCs has been demonstrated to play an essential role in eliciting cGVHD. We demonstrated that alloreactivity of T cells, especially CD4 T cells, can be recovered by suppressing RIDD in XBP-1s-deficient B cells (Fig. D). Since IRE-1α carrying a S729A mutation shows ablated RIDD activity without effect on splicing XBP-1 mRNA, we investigated the contribution of B cells from S729A knock-in mice to confirm the role of RIDD in B cells. We found that B cells from S729A mice increased GVHD severity (Fig. E). S729A B cells showed significant increases in IgM secretion (Fig. F), GC cell differentiation (Fig. G), and the expression levels of MHCII and co-stimulatory factors (Fig. H). In conclusion, these results provide a novel insight on how ER stress response regulates B cell activity after allo-HCT and suggest RIDD is an important mediator for reducing cGVHD pathogenesis.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.